Storage
Storage Services
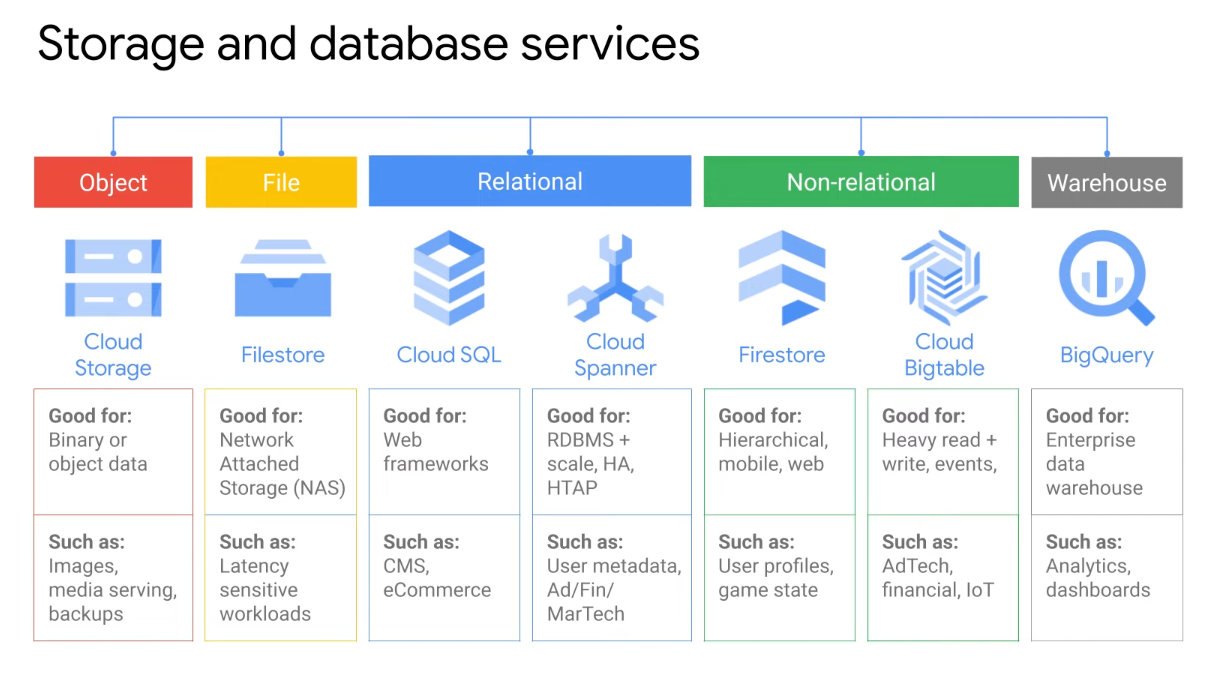
Characteristics
- SLAs
- Durability
- Scale
- Horizontally
- Bigtable
- Spanner
- Vertically
- Cloud SQL
- Memorystore
- Automatically
- Cloud Storage
- BigQuery
- Firestore
- Horizontally
- Consistency
- Everyone gets the latest copy of the data on reads
- Storage
- Cloud SQL
- Spanner
- Filestore
- Handle a large volume of writes
- Bigtable
- Memorystore replicas
- Everyone gets the latest copy of the data on reads

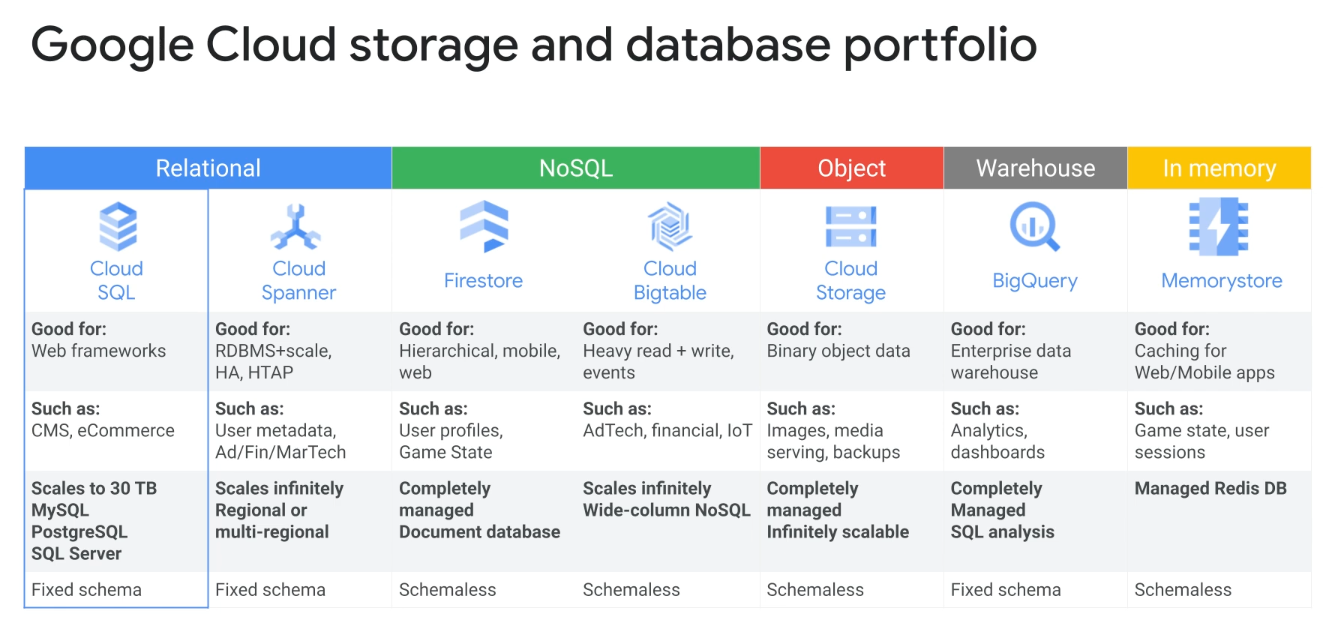
Cloud Storage
- Scalable to exabytes
- Time to the first byte in milliseconds
- Very high availability across all storage classes
- Single API across storage classes
- Automatic encryption
- Google Managed
- Customer managed - using Cloud Key Management Service
- Customer supplied - using the key created and managed by the customer
- The customer-supplied encryption key (CSEK)
- Object Versioning
- Maintain a history of modifications of objects
- List archived versions of an object, restore or delete.
- Object Lifecycle Management
- Can manage the classes of objects
- Retention policies specify a minimum retention period
- Object inspection occurs in asynchronous batches
- Changes can take 24 hours to apply
- Lifecycle policy
- Rules applied to buckets and content
- Actions executed when condition applies
- Lifecycle Actions
- Delete
- If versioned, deleting the live version creates a non-current version
- If versioned, deleing non-current version deletes the object permanently
- Change storage class based on age (can't change to the better class)
- Delete
- Lifecycle conditions
- Age
- Created before date
- Matches Storage Class
- Number of Newer Version
- Directory synchronization
- Max object size is 5TB
- Metadata for each file
- Object change notification
- Can use with pub/sub notifications for Cloud Storage
- Ramp up request rate gradually
- No problem up to 1000 write and 5000 read request per second, But more than this, take at least 20 minutes to double request rates
- Use
Exponential backoffif you receive 5xx (server error) or 429 (too many requests) (e.g. retry after 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, ... seconds) - Use Cloud Storage FUSE to enable file system access to Cloud Storage
Storage Class
- The default class is applied to new objects
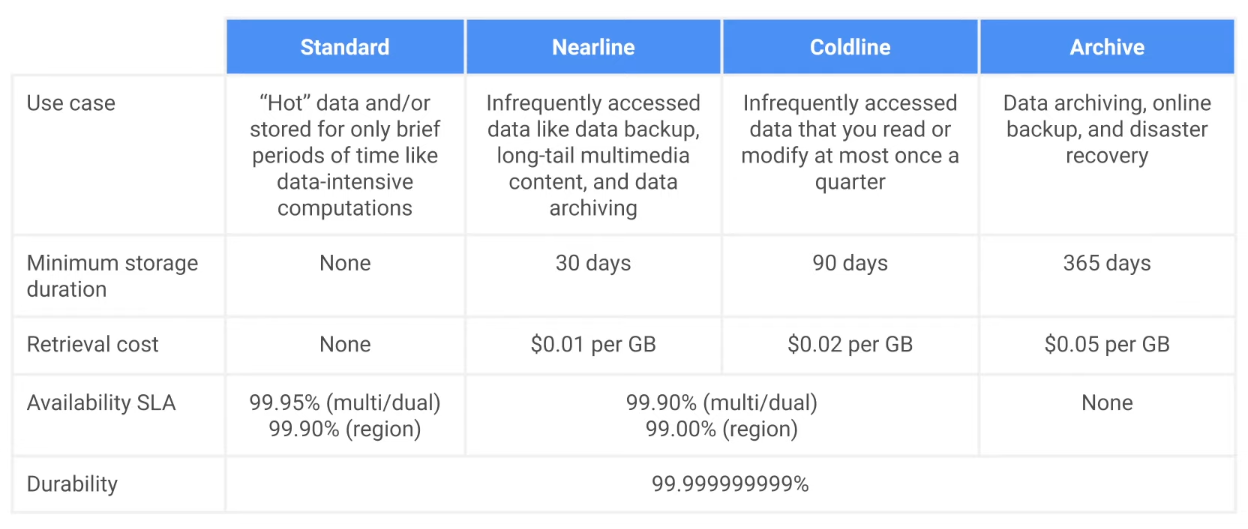
Redundancy
- Regional
- Data stored in a single region
- Replicated across zones
- Can't change to multi-region or dual-region
- Dual-region
- Data replicated across specific par of regions
- Auto-failover
- Multi-region
- Data duplicated across US, EU, or Asia
- Auto-failover
- Can't change to regional
Access Controls
Uniform bucket level access
- Recommended
- Use Cloud Identity and IAM
- Applies permissions to objects in a bucket or group of objects with a common prefix
Fine-grained
- Legacy access control method
- Uses ACLs
- ACL is a mechanism used to define who has access to your buckets and objects, as well as the level of access to have
- The maximum number of ACL entries you can create for a bucket or object is 100
- Each ACL consists of one or more entries, and these entries consist of two pieces of information
- A scope that defines who can perform the specified actions
- The permission defines what actions can be performed
- The
allUsersidentifier represents anyone who is on the Internet, with or without a Google account - The
allAuthenticatedUsersidentifier, in contrast, represents anyone who is authenticated with a Google account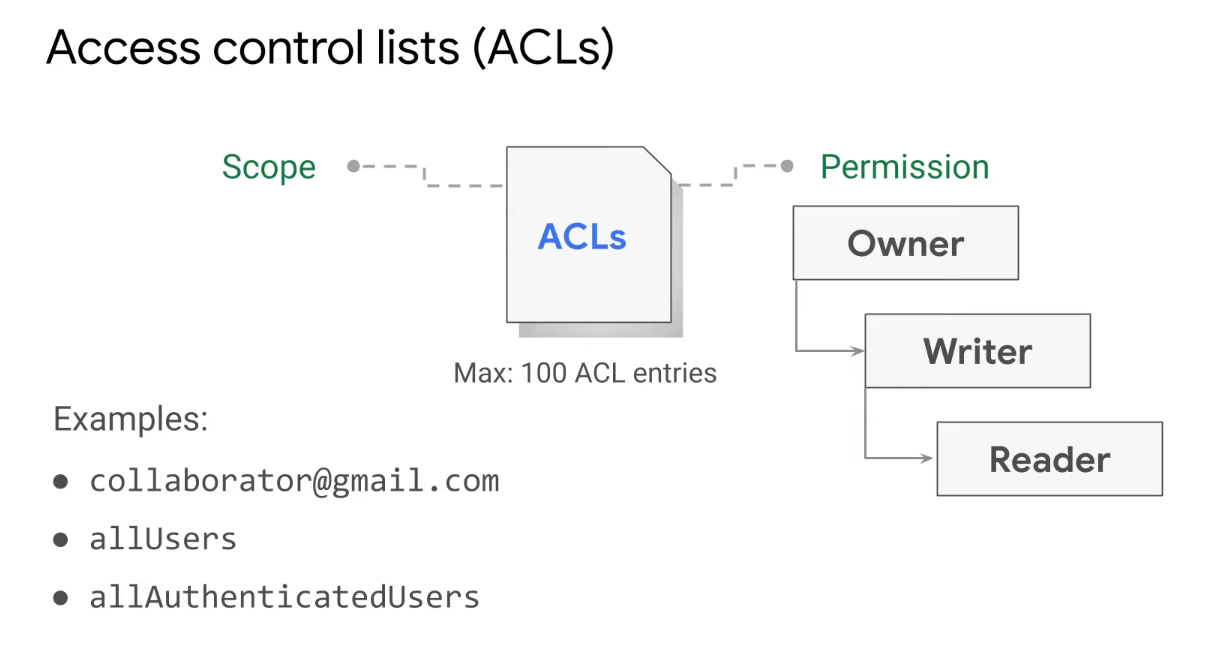
- Apply for permissions at both bucket and object level
Signed URLs
- Create a URL that grants read or write access to a specific cloud storage resource, and specifies when this access expires
- That URL is signed using a private key associated with their service account
- When the request is received, Cloud Storage can verify that the axis granting URL was issued on behalf of a trusted security principle
- "Valet Key" access to buckets and objects via ticket
- The ticket is a cryptographically signed URL
- Time-limited
- Operations specified in the ticket: HTTP GET, PUT, DELETE (not POST)
- Any user with a URL can invoke permitted operations
- Example:
gsutil signurl -d 10m path/to/privatekey.p12 gs://bucket/object
Data Import Services
Transfer Appliance
- Process
- Request Transfer Appliance
- Encrypt and copy your data
- Shop it back to Google
- Google loads the data
- You decrypt your data
- Capacity
- 40 TB
- 300 TB
- Rackable device up to 1PB
- Capture and then ship your data to Google Cloud
- Encryption key control by the customer
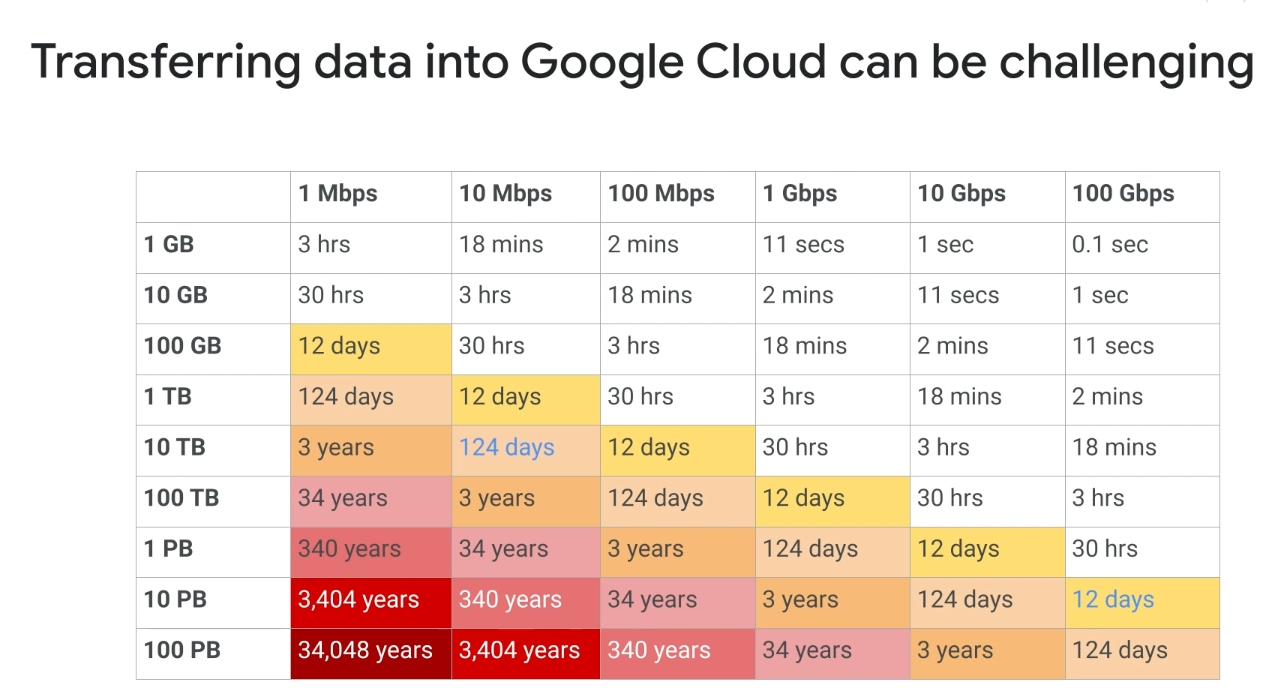
- Used when at least 10 TB of data or would take more than 1 week to load data
- Google securely erases the appliance after use


Storage Transfer Service
- Import online data
- Transfer between Cloud Storage buckets
- S3 bucket
- web source (HTTP/HTTPS location)
- Scheduled jobs
- One-time or recurring
- Options for deleting objects not in source or after transfer
- Filter on the file name, creation date
- On-premises agent
- Agent run in a Docker container
- Set up a connection to Google Cloud
- Requires a minimum of 300 Mbps bandwidth
- Scale to billions of files and 100s of TBs
- Automatic retires
- Logged
Offline Media Import
Third-party provider uploads the data from physical media
Filestore
- Fully managed network attached storage (NAS) for Compute Engine and GKE instances
- Predictable performance
- Full NFSv3 support
- HDD and SSD
- Scales to 100s of TBs for high-performance workloads
- Up to 320 TB with the throughput of 16 GB/s and 480K IOPS
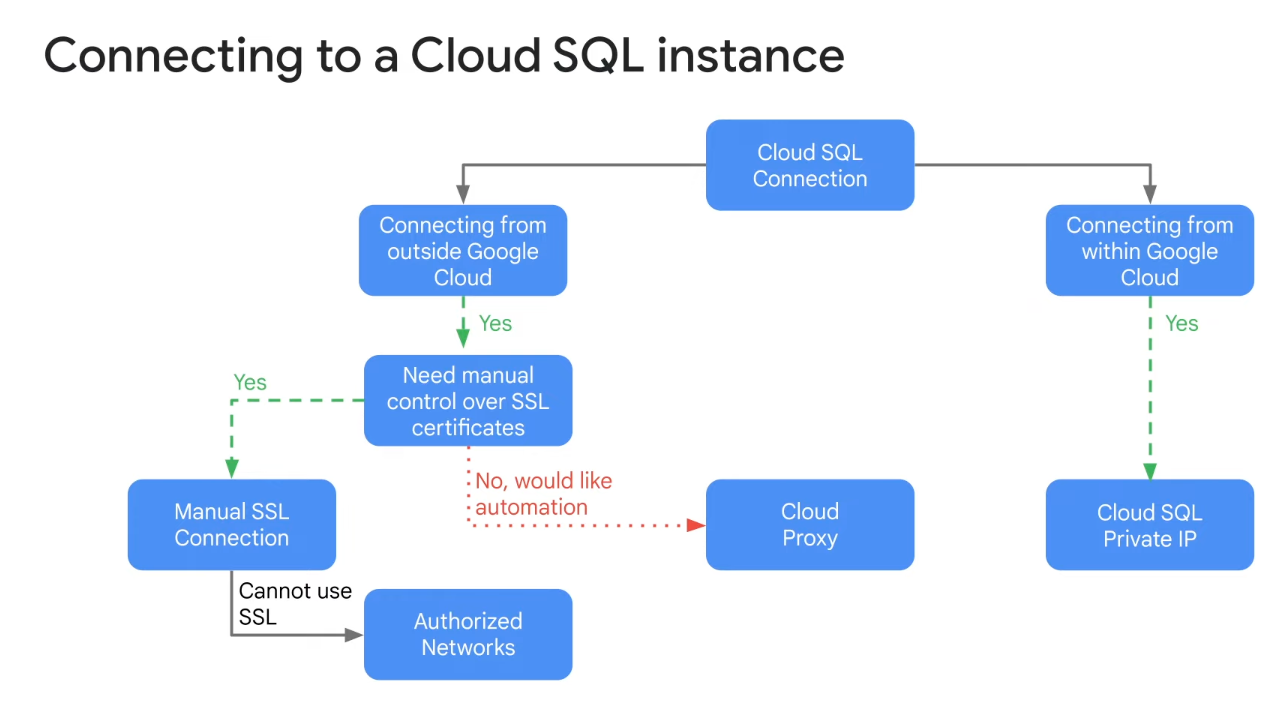
Cloud SQL
- Cloud SQL offers fully managed relational databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server as a service
- Designed to hand off mundane, but necessary and often time-consuming, tasks to Google—like applying patches and updates managing backups, and configuring replications
- Spec: 64 TB of Storage, 60000 IOPS, 624 GB of RAM
- Partitions shard data
- HA configuration
- Automatically fail-over (not revert automatically)
- HA setup can't be used as a read replica
- Geography
- Regional data store
- Multiple zones for high availability
- Multi-region for backups only
- Scale:
- Up: Machine capacity
- Out: Read replicas
- Choice:
- MySQL 5.6, 5.7 (default), or 8.0
- PostgreSQL 9.6, 10, 11, 12, 13 (default), or 14
- Microsoft SQL Server 2017 or 2019 (standard default)
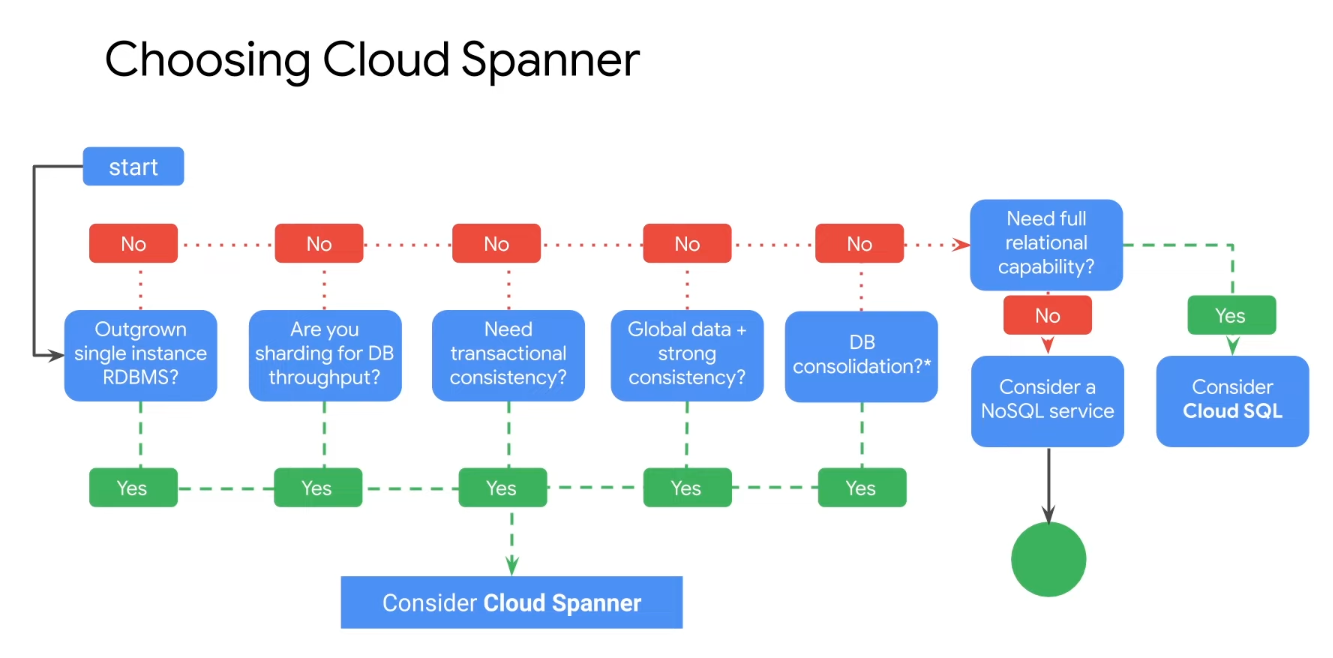
Cloud Spanner
- Cloud Spanner is a fully managed relational database service that scales horizontally, is strongly consistent, and speaks SQL
- Battle-tested by Google’s mission-critical applications and services, Spanner is the service that powers Google’s $80 billion business
- Cloud Spanner is especially suited for applications that require: A SQL relational database management system with joins and secondary indexes Built-in high availability Strong global consistency And high numbers of input and output operations per second
- Globally distributed and scalable
- Tens of thousands of reads and writes per second or more
- Scale to petabytes
- Used for financial and inventory applications
- Limitations
- 100 databases per instance
- Up to 2 TB per node
- 1000 tables per database
- 1024 columns per database
- 10MB maximum data per column
- 32 indexes per table
- 10000 indexes per database
- Uptime (Multi-regional: 99.999%, Regional: 99.99)
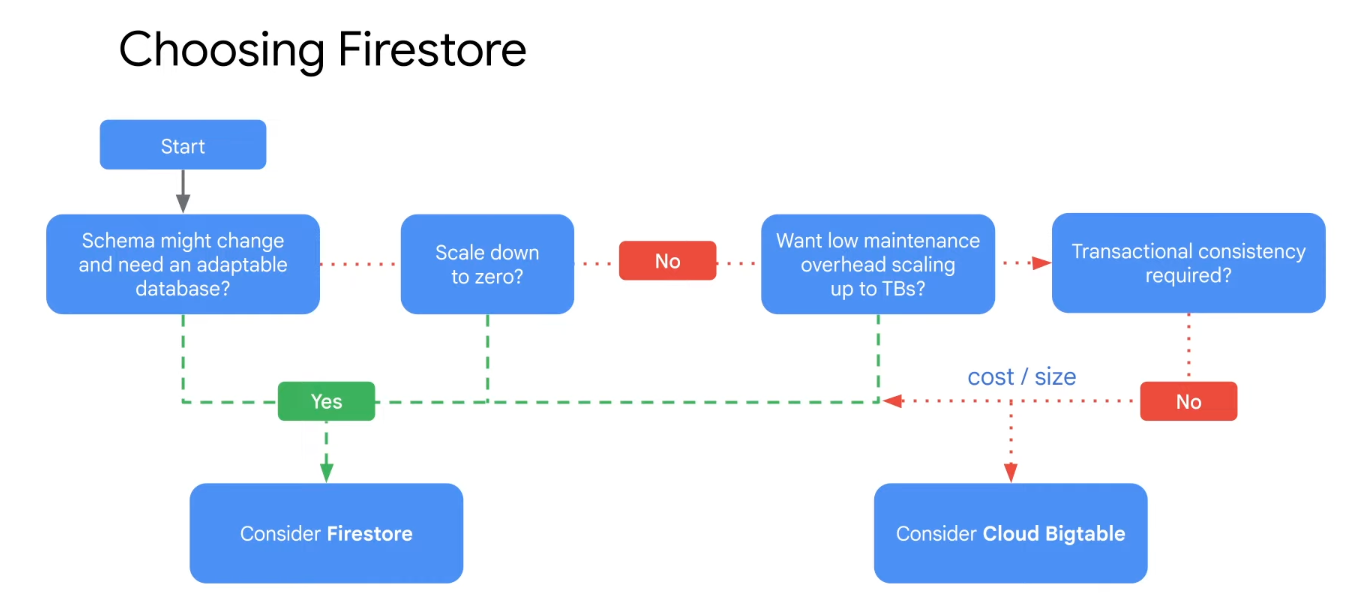
Cloud Firestore
- Firestore is a flexible, horizontally scalable, NoSQL cloud database for mobile, web, and server development
- With Firestore, data is stored in documents and then organized into collections
- Documents can contain complex nested objects in addition to sub-collections
- Firestore NoSQL queries can then be used to retrieve individual, specific documents or to retrieve all the documents in a collection that match your query parameters
- Queries can include multiple, chained filters and combine filtering and sorting options
- They're also indexed by default, so query performance is proportional to the size of the result set, not the dataset
- ACID transactions
- Multi-region replication
- Live synchronization and offline support
- Mode
- Datastore mode (server)
- backward compatible with Cloud Datastore
- No entity limits
- Used as Backend for server applications
- Native mode (mobile and web apps)
- Collection and document data model
- Real-time updates
- Used with mobile & web applications
- Datastore mode (server)
- Entities
- Describe or represent a thing
- A single entity is analogous to a row in a relational table
- A set of entities with similar attributes is somewhat analogous to a table in a relational database
- Entities have properties
- Related entities knowns as Kinds
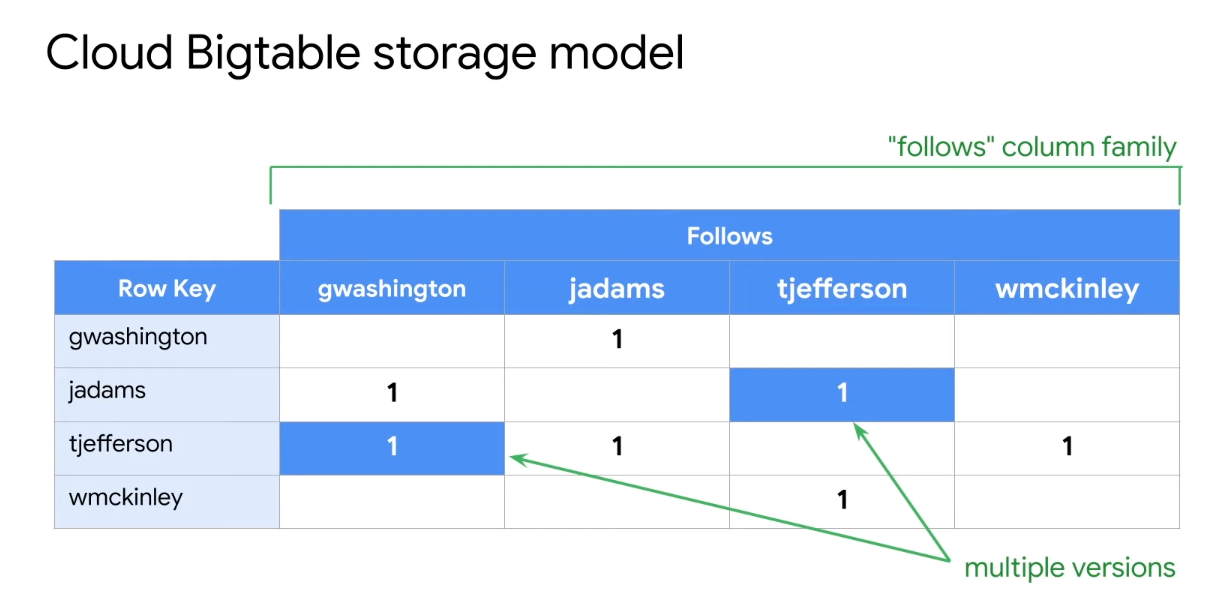
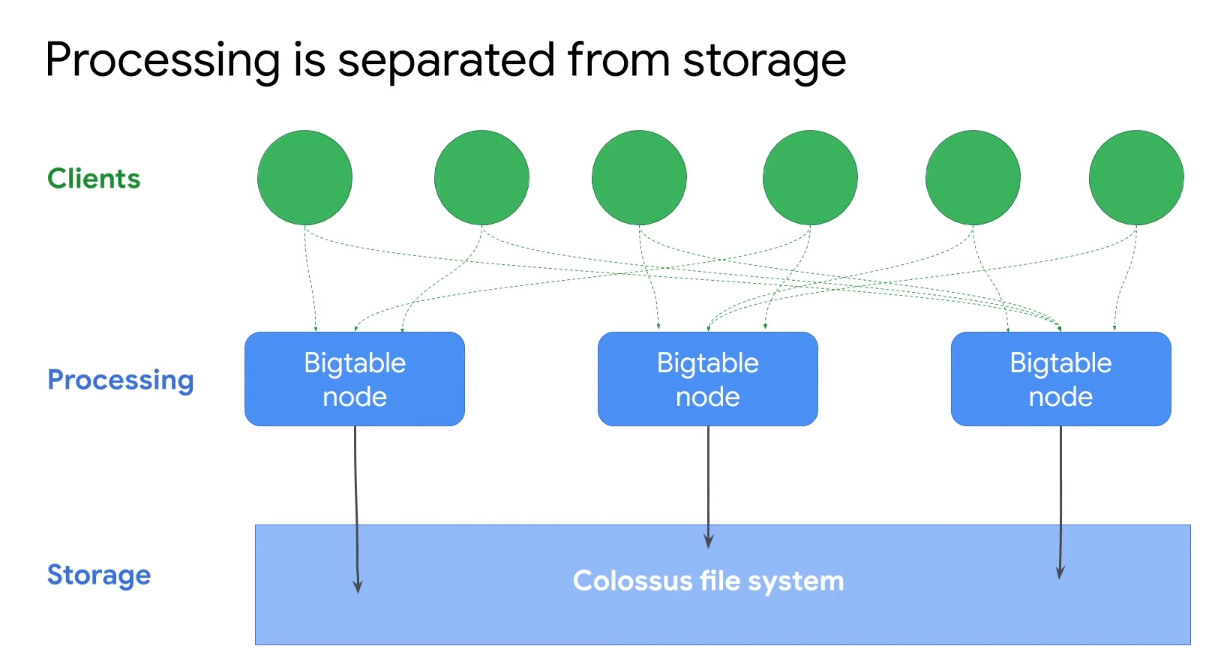
Cloud Bigtable
- Cloud Bigtable is Google's NoSQL big data database service
- The same database powers many core Google services, including Search, Analytics, Maps, and Gmail
- Bigtable is designed to handle massive workloads at consistently low latency and high throughput
- Wide column NoSQL DB
- HBase API compatible
- Not Serverless, Need to create an instance (use HDD or SSD)
- Can't export data using Cloud console or
gcloudcommand (Use java or HBase command) - Single-row transaction (multi-row transactions NOT support)
- Use
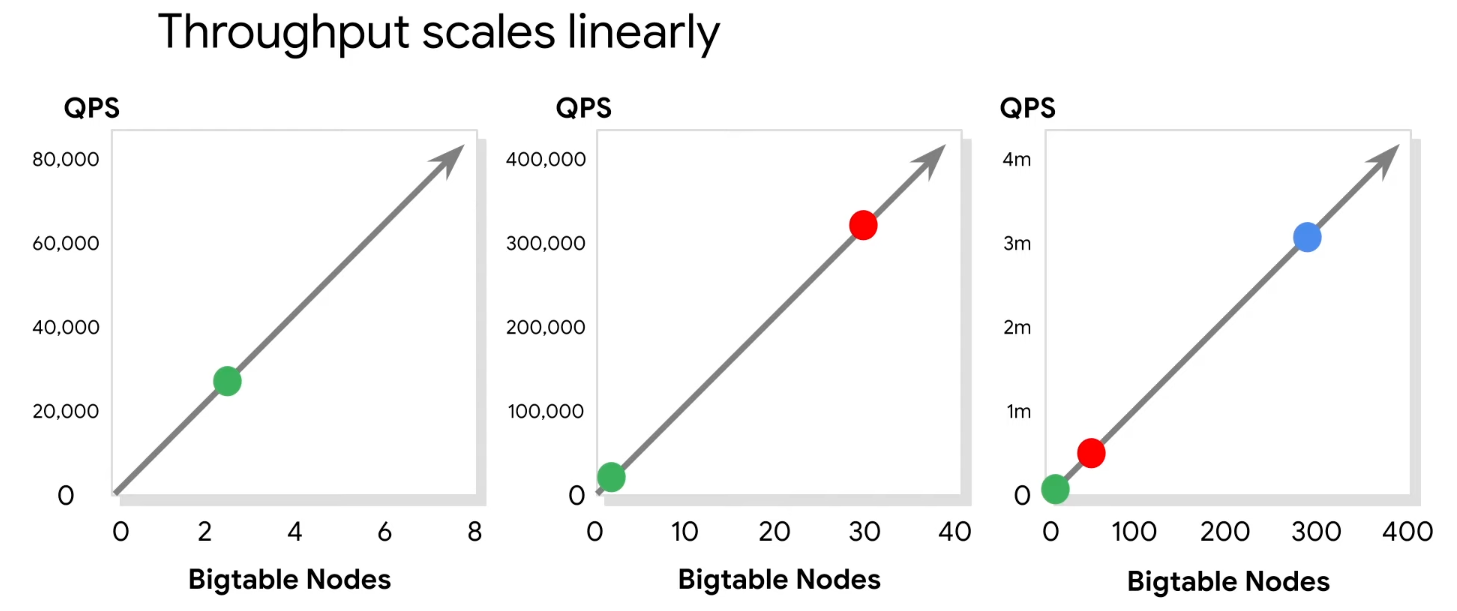
cbtto work with Bigtable - Petabyte-scale
- Consistent sub-10ms latency
- Seamless scalability for throughput
- Learns and adjusts to access patterns
- Ideal for Ad Tech, Fintech, Stream processing, ML, Analytics, and IoT
- Storage engine for MK applications
- Easy integration with open-source big data tools
- Batch MapReduce operations
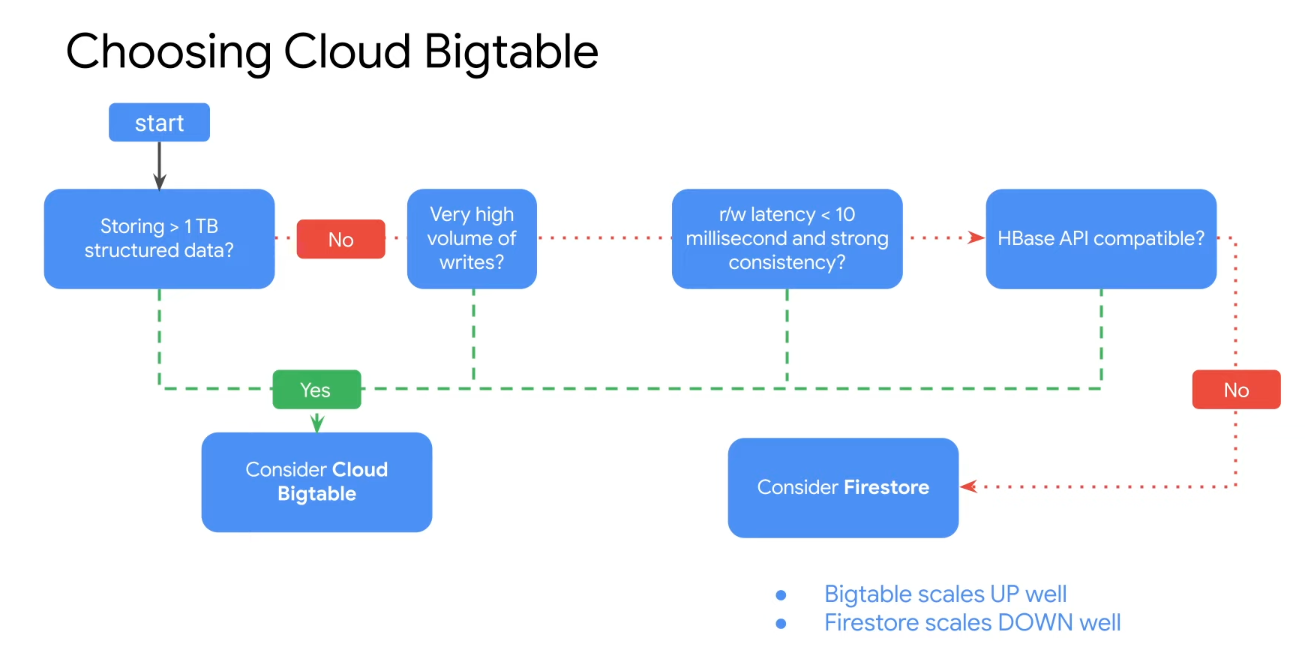
- Customers often choose Bigtable if: They’re working with more than 1TB of semi-structured or structured data
- Choose Bigtable when you have flat data that fit in one row per key, and when you need access latencies for your data to be in the millisecond range
Memorystore
- In-memory data store service
- High availability, failover, patching, and monitoring
- Sub-millisecond latency
- Instances up to 300 GB
- Network throughput of 12 Gbps
- Easy Lift-and-Shift
Cloud Datastore
- highly scalable NoSQL database for your web and mobile applications
- Firestore is the next generation of Datastore
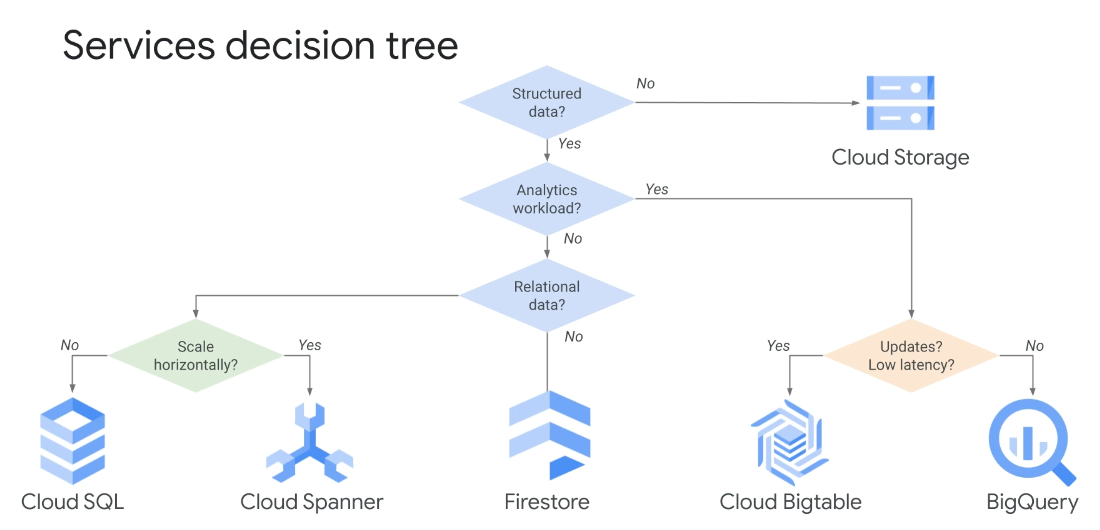
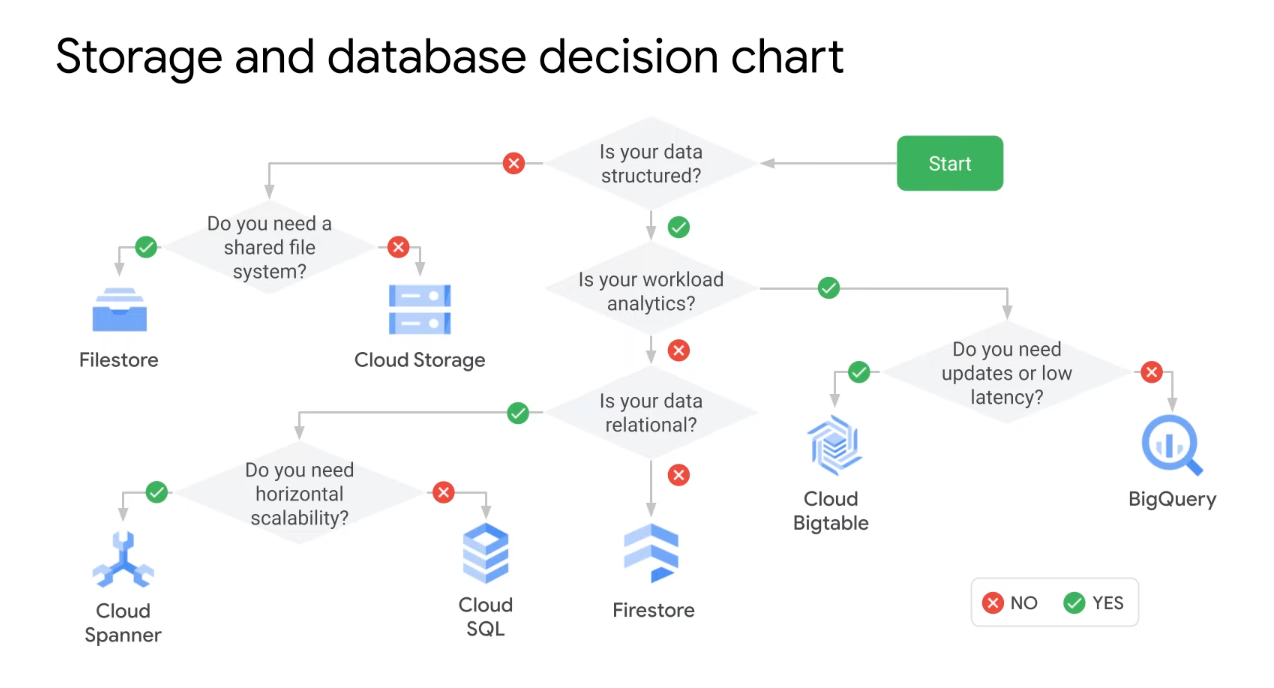
Decision Tree