Compute
Overview
Compute Engine
- Machine rightsizing
- Live migrate
- migrate the running instance to another host in the same zone
- Support for instances with Local SSDs
- Not Support for GPUs and preemptible instances
- Availability Policy
- On host maintenance
- Migrate (default)
- Terminate
- Automatic restart
- On host maintenance
- Auto restart
- Global load balancing
- OS patch management
- vCPU is equal to 1 hardware hyper-thread
- Sole-Tenant
- GPU
- Use images with GPU libraries (Deep Learning) otherwise, GPU will not be used
- restrictions
- NOT supported on all machine types
- host maintenance can only have the value "Terminate"
- TPU
- Use for massive matrix operations performed
- Machine families
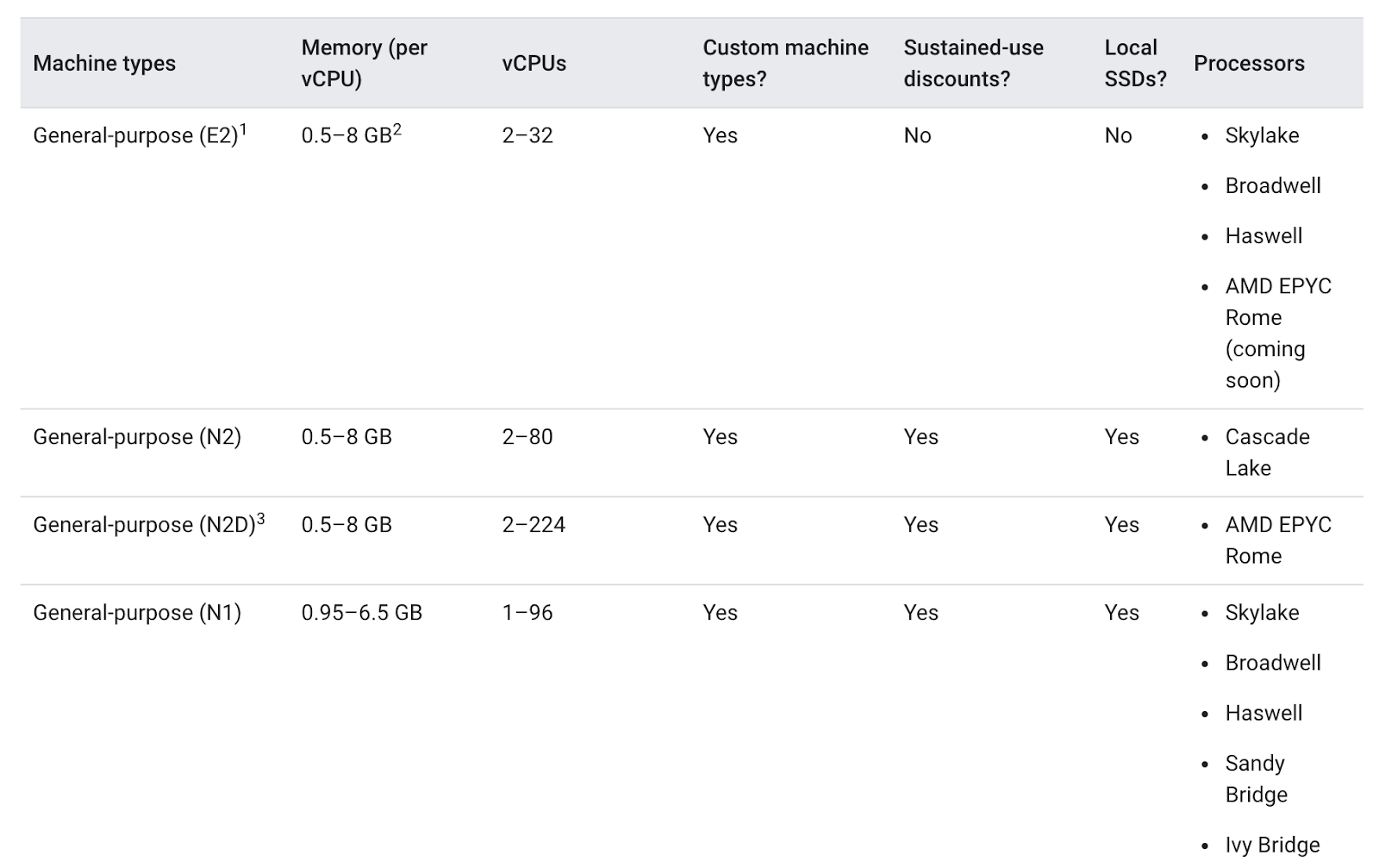
- General purpose (ratio of 0.5 GB to 8 GB of memory per vCPU)
- E2 (Cost-optimized)
- Standard (between 2 to 32 vCPUs)
- Shared-core (0.25 to 1 vCPUs, Context-switching)
- eg. Web serving, microservices, virtual desktop, small database
- N2 (Intel), N2D (AMD), N1 (Balanced price/performance)
- up to 128 vCPUs (Intel), up to 224 vCPUs (AMD)
- eg. cache, medium database, media/streaming
- Tau T2D (Scale-out optimized, Best performance/cost for scale-out)
- up to 60 vCPUs
- 4 GB of memory per vCPU
- eg. containerized microservices, large-scale java applications, media transcoding, scale-out workloads
- E2 (Cost-optimized)
- Compute-optimized (the highest performance per core)
- C2 (Ultra-high performance for compute-intensive workloads)
- 4 to 60 vCPUs
- up to 240 GB of memory
- up to 3 TB of local storage
- Offer all-core turbo
- eg. compute-bound workloads, gaming (AAA game servers), AI/ML, HPC (High-performance computing), Ad serving, media transcoding
- C2D
- 2 to 112 vCPUs
- 4 GB of memory per vCPU core
- 3TB of local storage
- eg. memory-bound workloads, Electronic Design Automation (EDA), high-performance database, media transcoding
- C2 (Ultra-high performance for compute-intensive workloads)
- Memory-optimized (higher memory-to-vCPU ratios)
- M1
- up to 4 TB of memory
- eg. MSSQL Server, in-memory database, in-memory analytics, business warehousing (BW) workloads, genomics analysis
- M2
- up to 12 TB of memory
- eg. Large in-memory databases such as SAP HANA, in-memory analytics, business warehousing (BW) workloads, and genomics analysis
- M1
- Accelerator-optimized
- A2
- 12 to 96 vCPUs
- up to 1360 GB of memory
- Each A2 machine type has a fixed number (up to 16) of NVIDIA’s Ampere A100 GPUs (40 GB of GPU memory)
- eg. CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) enabled ML training and inference, HPC, Massively parallelized computation
- A2
- Custom machine type
- It costs slightly more to use a custom machine type than an equivalent predefined machine type
- only machine types with 1 vCPU or an even number of vCPUs can be created. Memory must be between 0.9 GB and 6.5 GB per vCPU (by default)
- you can get more memory per vCPU beyond the 6.5 GB limit. This is referred to as extended memory
- General purpose (ratio of 0.5 GB to 8 GB of memory per vCPU)
- Shielded VMs
- Secure boot
- Virtual trusted platform module (vTPM)
- Integrity monitoring
- Required shielded image
- Confidential VMs
- Encrypts data while it's being processed
- Easy to use with no changes to code or performance compromise
- Running on N2D with AMD SEV (Secure Encrypted Virtualization)
- Image
- Premium image indicated in parentheses with a p. eg. RHEL(p)
- These images will have per-second charges after a one-minute minimum. With the exception of sequel server images, which are charged permanently after a 10-minute minimum.
Persistent Disks
- Standard and SSD PDs scale in performance for each GB
- Resize or migrate instances with no downtime
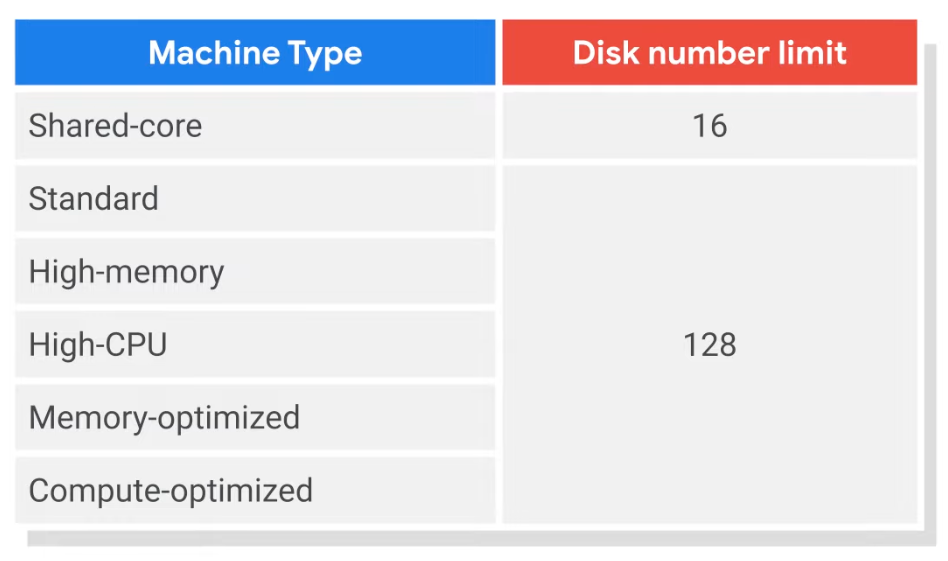
- Local SSD can create up to 8 partitions per instance with 375 GB (Total 3TB)
- Standard and non-local SSD can be sized up to 257 TB for each instance
- Attach read-only for multiple VMs
- Types
- Local SSD
- Temporary data - Data persists until the instance is running
- Enable live migration for data to survive maintenance events
- Lifecycle tied to the VM instance
- Can't configure encryption keys
- Only some machine support
- Supports SCSI and NVMe interfaces
- Choose NVMe-enabled and multi-queue images for the best performance
- Larger Size, More vCPU = Better Performance
- Persistent Disks
- Options: Regional and Zonal
- Regional PDs are 2X the cost of Zonal PDs
- Independent lifecycle from the VM instance
- Performance scales with size
- Lifecycle NOT tied to the VM instance
- Type
- pd-standard (HDD)
- pd-balanced (SSD)
- pd-ssd (SSD)
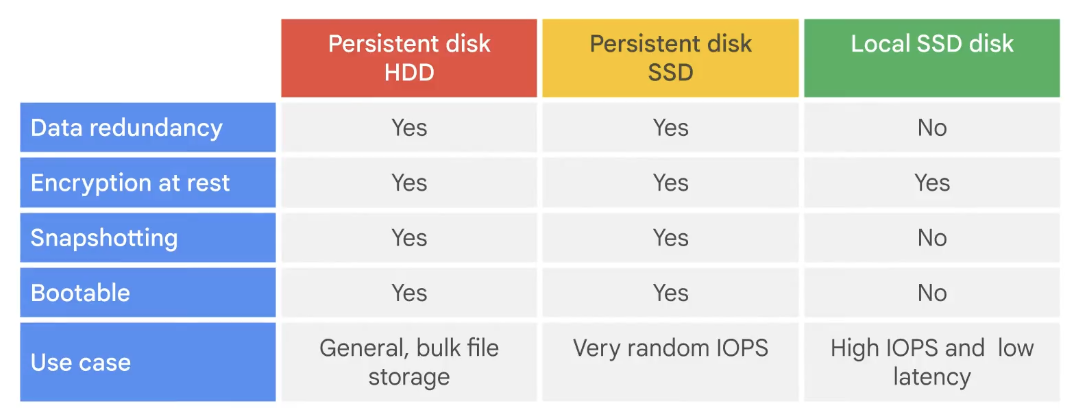
- Local SSD
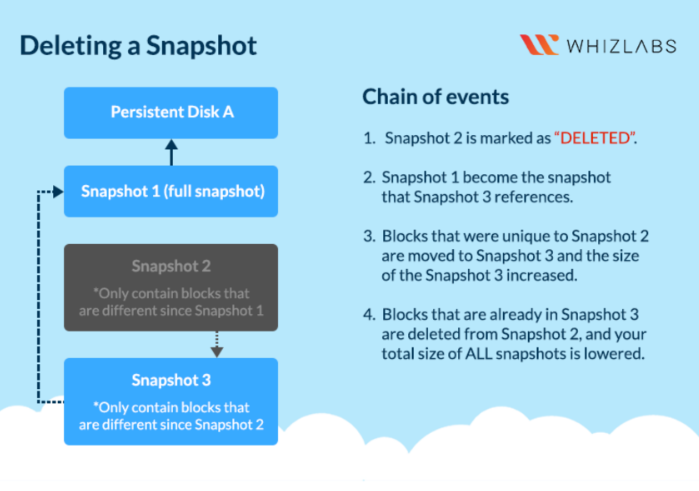
Snapshot
- Take point-in-time snapshots of your Persistent Disks
- Schedule snapshots (support auto-delete after X days)
- Snapshots can be Multi-regional and Regional
- Share snapshots across projects
- Snapshots are incremental
- Snapshots reduce performance (schedule during off-peak hours)
Networking
- Network throughput scales at 2 Gbps per vCPU
- Max 32 Gbps with 16 vCPU
- Up to 8 NICs connected to different network
- Each NIC must be attached to a different VPC
- Can't modify after creation
Pricing
- Per-second billing, with a minimum of 1 minute
- Resource-based pricing: each vCPU and memory is billed separately
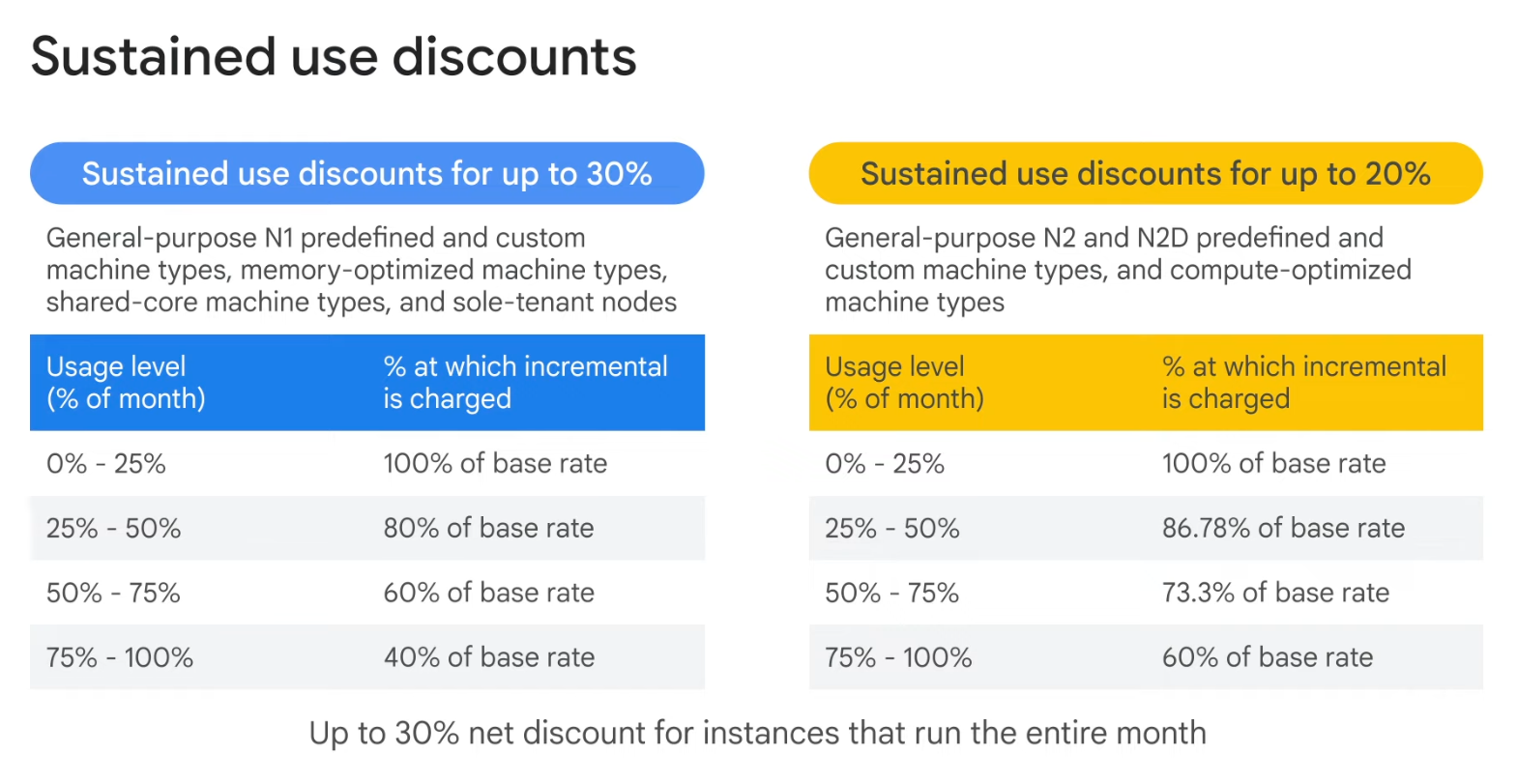
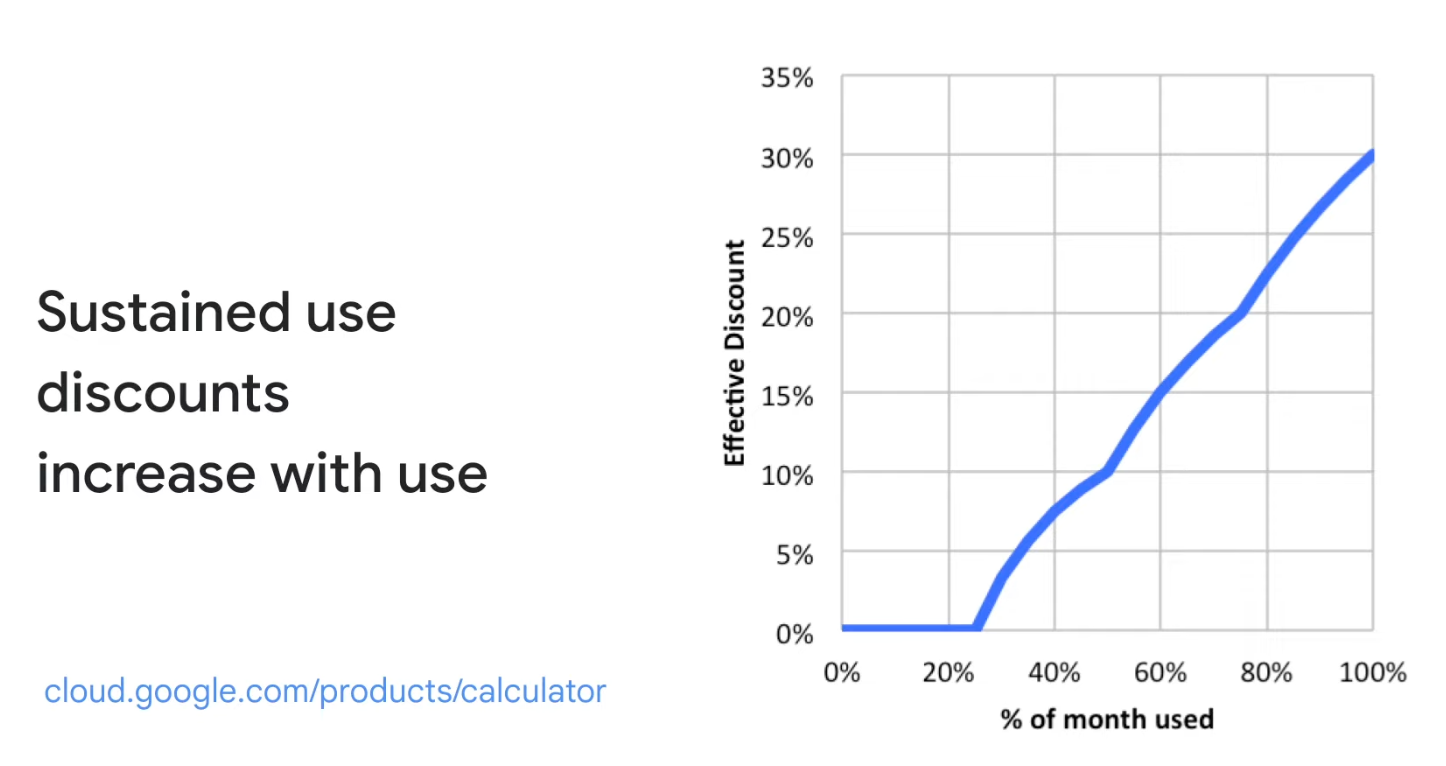
- Discounts
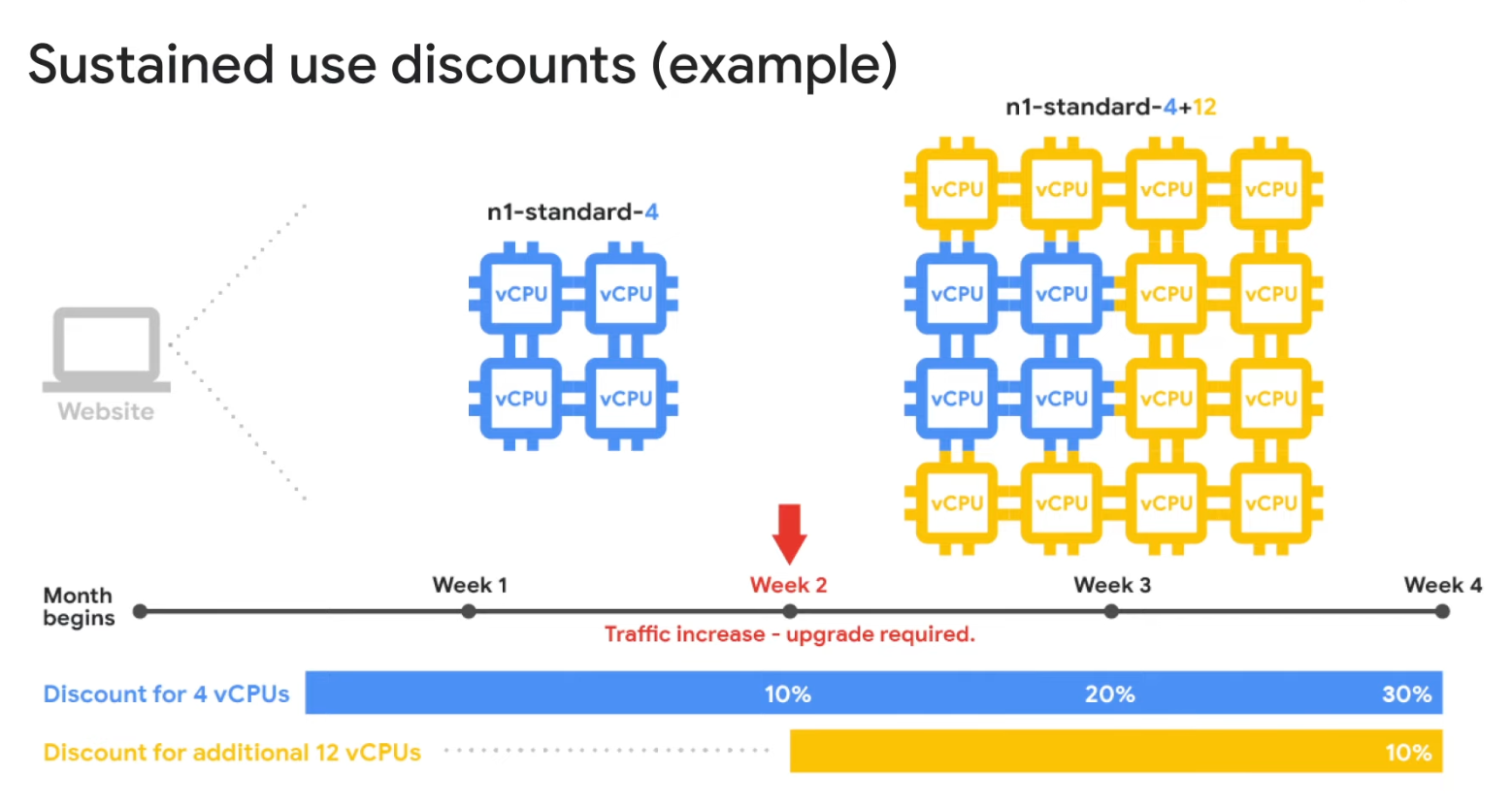
- Sustained use
- If using more than 25% of a month, You will get a 20% to 50% discount on every incremental minute
- Applicable for GKE and Compute Engine
- Committed use
- For predictable resource needs
- up to 57% for most machine types
- up to 70% for memory-optimized machine types
- Applicable for GKE and Compute Engine
- Preemptible VM
- Up to 91%
- 30-second stop warning, but not guaranteed
- 24 hours max
- Free tier credits are not applicable
- no live migration; no auto restart
- Spot VM
- the latest version of preemptible
- 30-second notice to be reclaimed at any time
- Dynamic pricing 60-91% discount
- Free tier credits are not applicable
- no maximum runtime
- no live migration; no auto restart
- Sustained use
- Recommendation Engine
- Notifies you of underutilized instances
- recommendations for the new instance will appear 24 hours after the instance has been created
- Free usage limits
- Sustained use discounts are automatic discounts that you get for running
Managed Instance Groups
- Deploy identical instances based on the instance template
- The instance group can be resized
- The manager ensures all instances are RUNNING
- Typically used with autoscaler
- Can be a single zone or regional
- Rolling update without service disruption
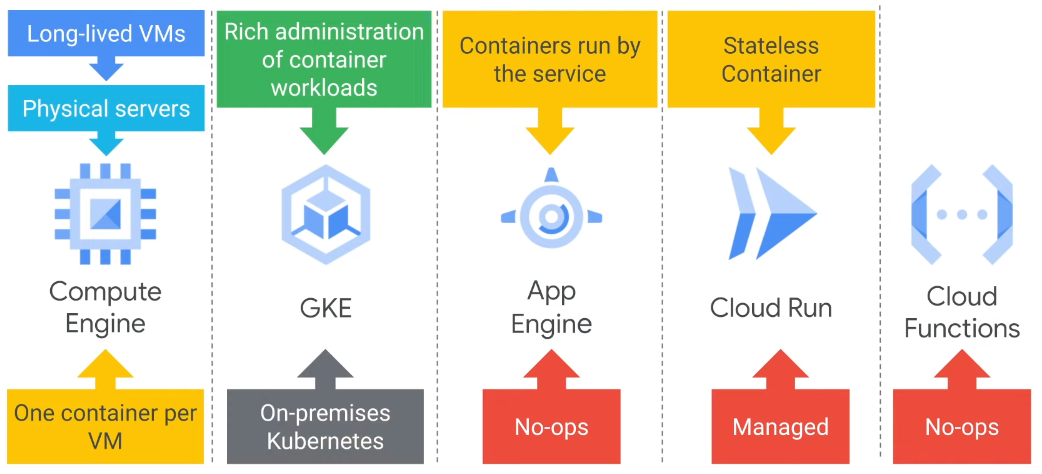
GKE
- Fully managed Kubernetes
- Container-Optimized OS
- Auto upgrade
- Auto repair unhealthy node
- Cluster autoscaling
- Seamless integration with Cloud Build and Container Registry
- Identity and access management
- Integrated logging and monitoring with Google Cloud Operation Suite
- Integrated networking with VPC features
- Cloud Console can view, inspect, and delete the resources
- Stream log to Cloud Logging by default
- Node-level logging that is older than 1 day or reaches 100 Mb will be compressed and rotated
- Binary authorization allows you to enforce deployment of only trusted containers into GKE
- Number of nodes per region
- Mode
- Standard
- Pay per resources provisioned
- User configured resources
- User Configured autoscaling
- Regional or zonal
- Autopilot
- Google manages nodes and pools
- Provision based on pod specification
- Pay per pod, only resources used
- Built-in security best practices
- Regional
- Standard
Node Auto Provisioning (NAP)
- Adds new node pools sized to meet demand
- Without node auto-provisioning, the cluster autoscaler will only create new nodes in the node pools you specified, meaning the new nodes will be the same machine type as the other nodes in that pool
- This is perfect for helping optimize resource usage for batch workloads and other apps that don't need extreme scaling
- Creating a node pool specifically optimized for your use case might take more time than just adding more nodes to an existing pool
Network policy
- Requirements
- Have at least 2 nodes
- The node must restart when to enable
- All nodes must be of machine type
n1-standard-1or higher
Double-Hop problem
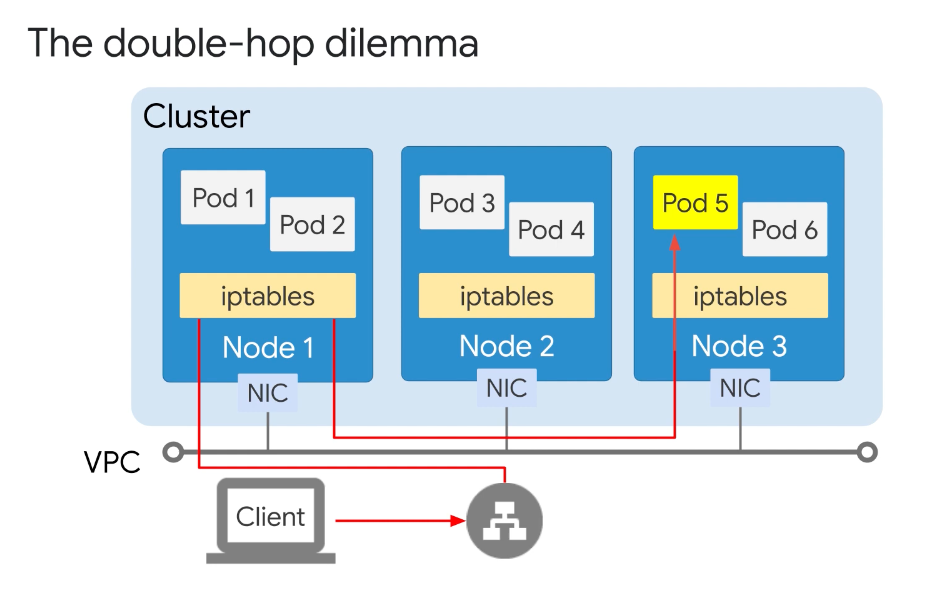
- Set
externalTrafficPolicy: localin the service manifest to force thekube-proxyto choose a Pod on the receiving node for the lowest latency
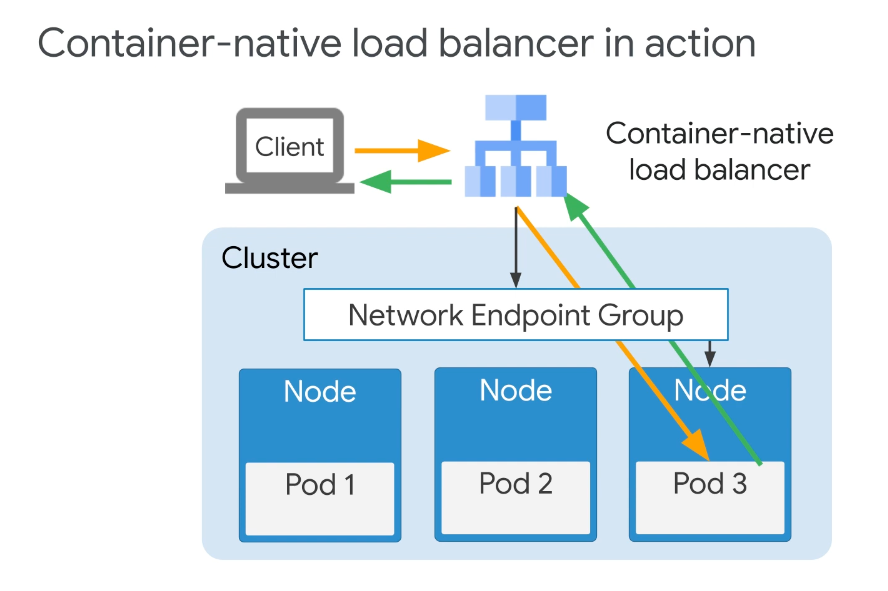
Container-native load balancer
- eliminates the "Local" external-traffic policy workaround
- Leverages a Google Cloud HTTP(S) load balancer
- Traffic is directed to the Pods directly instead of to the nodes
- Use a data model called Network Endpoint Groups
Workload Identity
- Access Google Cloud services in a secure and manageable way
- Workload Identity allows a Kubernetes service account in your GKE cluster to act as an IAM service account
- Pods that use the configured Kubernetes service account automatically authenticate as the IAM service account when accessing Google Cloud APIs
App Engine
- Provides a fully managed, code-first platform
- Streamlined application deployment and scalability
- Support popular programming languages and application runtimes
- Simplifies version control canary testing, and rollbacks
- Scaling mode
- Automatic - Create instance based on request rate, response latencies, and other metrics
- Basic - Create instance when receiving requests, shutdown when idle
- Manual
- Standard Mode
- Run in seconds with preconfigured containers
- The application run in a secure sandbox
- no SSH access
- no write on disk (maybe /tmp available)
- network access via App Engine
- pay per instance (hours) class with automatic shutdown
- Can scale to zero instance
- Standard runtimes: Python, Java, Node, Go, PHP, and Ruby
- Max Request timeout 1 to 10 minutes
- Flexible Mode
- Run in minutes with customized Docker containers
- SSH accessible (Not restricted as sandbox used in Standard mode)
- Access resources in Compute Engine
- ephemeral disk
- Can access without App Engine network
- Pay per hour based on vCPU, Memory, and persistent disks
- Minimum 1 instance
- No automatic shutdown
- Max Request timeout 60 minutes
- Configured in
app.yamlTarget_cpu_utilizationTarget_throughput_utilizationMax_concurrent_requestsMax_pending_latencyMin_pending_latency
- Traffic Splitting
- IP Address
- HTTP cookie
- Random
- One Application per project
App Engine Memcache
- Memcache for App Engine
- Ephemeral data
- Mode
- Shared (free)
- Dedicated
Cloud Run
- A managed-to-compute platform that can run the stateless containers
- Serverless, removing the need for infrastructure management
- Built on Knative, an open API and runtime environment built on Kubernetes
- Automatically scale up and down from zero almost instantaneously charging only for the resources used
- Pay-per-use
- Up to 1000 container instances by default
- Manage identities that can access service or allow unauthorized access
- Containers isolated to gVisor sandbox
- Container instance can receive up to 80 requests at the same time (1,000 max)
- Possible to reduce concurrency to 1
Cloud Function
- Cloud Functions is a lightweight, event-based, asynchronous compute solution that allows you to create small, single-purpose functions that respond to cloud events, without the need to manage a server or a runtime environment
- Charges apply only when your code runs
- Automatic scaling with highly available and fault-tolerant design
- Triggered based on events in Google Cloud services, HTTP endpoints, and Firebase
- Receive 1 request at a time
- Trigger types
- HTTP
- Cloud Storage
- Cloud Pub/Sub
- Cloud Firestore
- Firebase
- Cloud Logging
- No internet access by default
- Best practices
- Correctness
- Write idempotent functions
- Send HTTP response in HTTP functions
- Do not start background operations
- Clean up temporary files
- Do not manually exit, e.g. do not use
sys.exit()in Python
- Performance
- Balance the use of imports with performance
- Use global variables to reuse variables across invocations
- Use lazy initialization on global variables
- Correctness
- Generation
- V1
- 1 concurrent request per function instance
- Up to 8 GB with 2 vCPU
- Support 4 event types
- V2
- Build on top of Cloud Run and Eventarc
- Recommended
- Request timeout up to 60 minutes for HTTP triggered
- Up to 16 GiB with 4 vCPU
- Up to 1000 concurrent per function instance
- Support Multiple Function Revisions and Traffic Splitting
- Support for 90+ event types
- V1
- Typical serverless functions architecture
- Autoscaling as new invocations com in
- One function instance handles ONLY ONE request at a time
- Cold Start
- Solution - Configure Min number of instances (increases cost)
Pub/Sub
- The publisher sends a message to Topic
- Message individually delivered to each and every subscription
- Subscribers can receive messages either by push and pull
- Add Dataflow into flow to enable message deduplication (exactly-once processing)
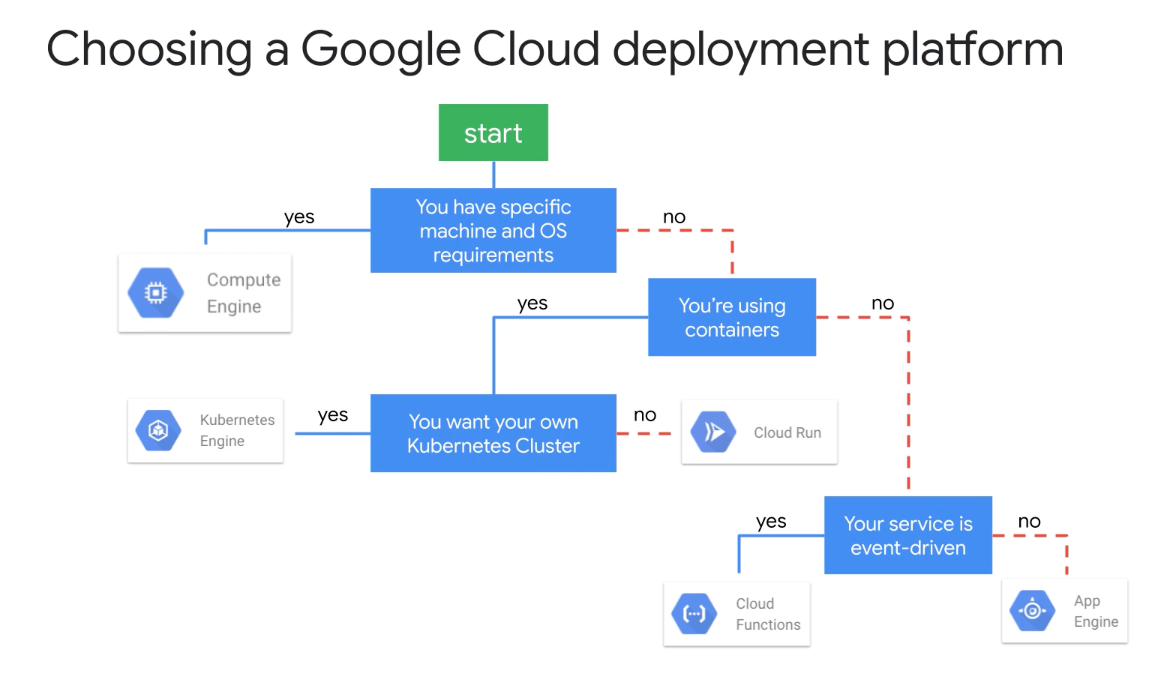
Decision Tree